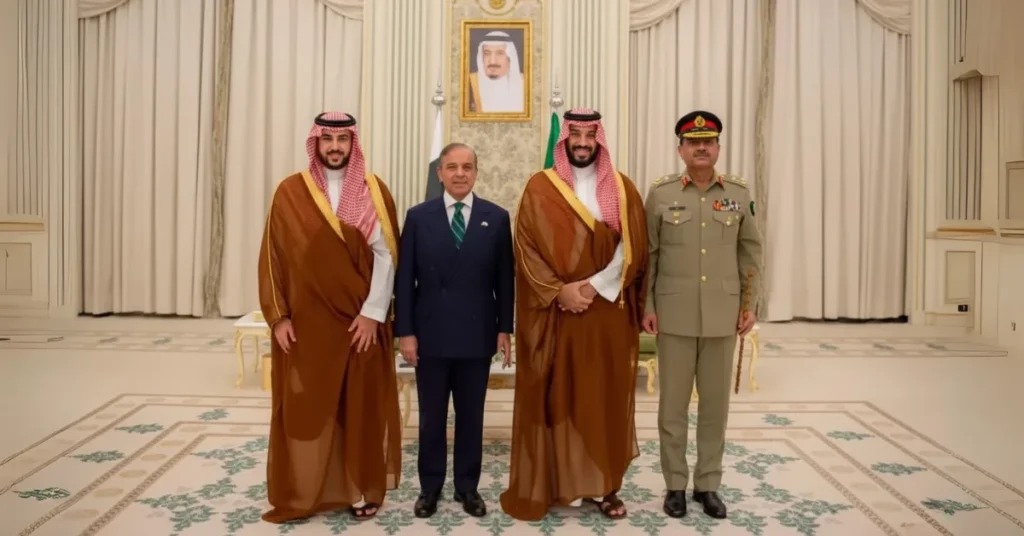
The September 17, 2025 signing of the Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia marks a pivotal moment in international relations, fundamentally altering Middle Eastern security dynamics and global power structures. This comprehensive defense pact between the Islamic world’s only nuclear-armed state and the custodian of Islam’s holiest sites represents the most significant regional security realignment since the Cold War’s conclusion.
The Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement: Comprehensive Framework Analysis
The Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement was formalized at the Royal Court in Al-Yamamah Palace, Riyadh, establishing unprecedented bilateral defense cooperation between two major regional powers.
Agreement Architecture and Key Provisions
| Component | Specification | Strategic Significance |
| Agreement Title | Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement | Indicates comprehensive security partnership |
| Execution Date | September 17, 2025 | Strategic timing following regional security crisis |
| Venue | Al-Yamamah Palace, Royal Court, Riyadh | Highest-level diplomatic protocol |
| Primary Signatories | Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman (Saudi Arabia), Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif (Pakistan) | Supreme executive authority engagement |
| Military Witness | Field Marshal Asim Munir (Pakistan Army Chief) | Direct military-to-military commitment |
| Core Defense Principle | “Any aggression against either nation constitutes aggression against both” | Establishes NATO Article 5-equivalent collective defense |
The agreement establishes a comprehensive defense framework encompassing multiple operational dimensions:
Military Cooperation Enhancement:
- Expanded joint military exercises incorporating advanced warfare scenarios
- Systematic personnel exchange programs across all service branches
- Standardized operational procedures and tactical coordination protocols
- Advanced weapons systems training and technology transfer initiatives
Intelligence Integration Framework:
- Real-time intelligence sharing between Pakistan’s ISI and Saudi Arabia’s GIP
- Joint threat assessment and analysis capabilities
- Coordinated counter-terrorism and counter-intelligence operations
- Shared early warning systems for regional security threats
Defense Industrial Collaboration:
- Joint research and development programs for indigenous defense capabilities
- Technology transfer agreements bypassing Western restrictions
- Collaborative manufacturing initiatives for defense equipment
- Shared procurement strategies reducing external supplier dependence
Regional Security Mandate:
- Coordinated crisis response mechanisms for Middle East and South Asia
- Joint diplomatic initiatives for conflict prevention and resolution
- Humanitarian cooperation during regional emergencies
- Collective approach to regional stability maintenance
Pakistan, as the world’s only nuclear-armed Muslim nation, now formally allies with Saudi Arabia, one of the Middle East‘s most influential kingdoms, creating a formidable strategic partnership with global implications.
Geopolitical Context: Israel’s Qatar Strike and Security Paradigm Shift
The agreement’s timing directly correlates with fundamental shifts in regional security calculations triggered by Israel’s unprecedented September 9, 2025 attack on Qatar.
The Qatar Attack: Strategic Catalyst Analysis
Israel’s airstrike on Hamas leadership in Doha represents a watershed moment in Gulf security perceptions:
Operational Details:
- Target: Hamas political leadership engaged in ceasefire negotiations
- Location: Qatar’s diplomatic quarter in Doha
- Casualties: Five Hamas officials and one Qatari security officer eliminated
- Strategic Context: Attack occurred despite Qatar hosting U.S. Central Command headquarters
Regional Security Implications: The strike fundamentally undermined Gulf Cooperation Council confidence in American security guarantees. Qatar hosts approximately 10,000 U.S. military personnel at Al Udeid Air Base, serving as forward headquarters for U.S. Central Command operations across the Middle East. Israel’s ability to conduct military operations against a key American ally while U.S. forces were present exposed critical limitations in traditional security arrangements.
Gulf States’ Security Recalculation
The Qatar attack triggered immediate institutional responses:
- Emergency Arab League and Organization of Islamic Cooperation sessions
- Gulf Cooperation Council activation of joint defense mechanisms
- Systematic reassessment of U.S. security guarantee reliability
- Acceleration of alternative security partnership development
Dr. Muhammad Faisal, University of Technology Sydney, analyzes the broader transformation: “These developments have fundamentally exacerbated Gulf states’ security anxieties while undermining confidence in the U.S. security umbrella’s effectiveness. Consequently, Gulf nations are increasingly viewing regional powers such as Pakistan, Turkey, and Egypt as viable security partners.”
Nuclear Dimensions: Strategic Deterrence and Extended Nuclear Umbrella

The nuclear aspect represents the agreement’s most strategically consequential element, generating intense international scrutiny and analysis.
Pakistan’s Nuclear Capabilities Assessment
Pakistan operates a sophisticated nuclear weapons complex with diverse delivery systems:
| Delivery System | Technical Specifications | Strategic Application | Regional Coverage |
| Shaheen-I (Hatf-IV) | Range: 750km, Single warhead, Road-mobile | Regional deterrence | Iranian territory from Pakistani bases |
| Shaheen-II (Hatf-VI) | Range: 1,500km, Single warhead, Advanced guidance | Extended regional deterrence | Comprehensive Middle Eastern coverage |
| Shaheen-III (Hatf-VII) | Range: 2,750km, Single warhead, MIRV-capable | Strategic deterrence | Israeli territory from Pakistani soil |
| Ababeel (Hatf-VIII) | Range: 2,200km, MIRV capability, Penetration aids | Advanced deterrence | Defeats sophisticated missile defenses |
| Babur-3 | Range: 450km, Nuclear-capable, Submarine-launched | Sea-based deterrence | Eliminates range limitations through naval deployment |
| Nasr (Hatf-IX) | Range: 60-70km, Low-yield tactical, Mobile | Battlefield deterrence | Limited tactical application |
Nuclear Deterrence Evolution and Extended Protection
Pakistani Defense Minister Khawaja Asif’s declaration that Pakistan’s capabilities will “absolutely” be available under the agreement suggests significant nuclear doctrine expansion.
Extended Deterrence Framework Analysis: The nuclear umbrella concept operates through established deterrence theory:
- Capability Demonstration – Pakistan possesses sufficient nuclear forces for credible deterrence
- Alliance Credibility – Formal defense treaty creates believable commitment to Saudi defense
- Strategic Uncertainty – Adversaries must factor Pakistani nuclear response into Saudi targeting calculations
- Deterrent Psychology – Alliance relationship influences enemy risk assessment and decision-making
Former Pakistani diplomat Hussain Haqani emphasizes terminological significance: “The agreement’s designation as ‘Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement’ carries specific meaning within Pakistani strategic culture, where ‘strategic’ traditionally refers to nuclear weapons and delivery systems.”
Expert Analysis on Nuclear Implications
Nuclear Security Specialist Dr. Rabia Akhtar (Belfer Center) provides a comprehensive assessment: “This pact formalizes a historically deep alliance rather than creating unprecedented arrangements. It simultaneously reassures Saudi citizens of Pakistani commitment, warns potential adversaries of Saudi alliance backing, and signals to the United States the importance of Gulf security concerns.”
Skeptical Technical Analysis: Security Analyst Sahar Khan challenges nuclear umbrella assumptions: “The agreement contains no explicit provisions indicating nuclear protection umbrella formation or extended deterrence arrangements. Pakistan’s nuclear doctrine maintains its traditional India-centric focus.”
Strategic Range Assessment: Research Fellow Hussain Abdul-Hussain (Foundation for Defense of Democracies) questions technical feasibility: “Pakistani nuclear umbrella provision remains technically questionable given the Shaheen-III’s 2,750-kilometer maximum range, insufficient for addressing numerous potential Saudi threats. Pakistan lacks demonstrated capability for decisive nuclear power projection across the 2,600-mile distance to Riyadh.”
Regional Power Dynamics: Strategic Balance Transformation

The defense agreement fundamentally alters Middle Eastern and South Asian power structures, creating new strategic equilibriums and tensions.
Impact on India-Pakistan Relations
The agreement arrives at a particularly sensitive moment in India-Pakistan relations, following their May 2025 four-day military confrontation.
May 2025 Conflict Analysis:
- Duration: Four-day military engagement representing most serious escalation since 1999
- Trigger: Pahalgam attack resulting in 26 civilian casualties in Indian-administered Kashmir
- Military Operations: Artillery exchanges, limited airstrikes, border infiltration attempts
- Resolution: U.S.-mediated ceasefire, though fundamental tensions remain unresolved
Strategic Implications for India:
Military Balance Disruption:
- Saudi Arabia’s $700+ billion Public Investment Fund enables potential Pakistani defense modernization
- Enhanced intelligence coordination between Saudi GIP and Pakistani ISI regarding Indian activities
- Saudi diplomatic support for Pakistani positions in international forums
- Potential Saudi investment in Pakistani missile and nuclear delivery system development
Economic Leverage Complications:
- Saudi capacity for economic pressure supporting Pakistani strategic objectives
- India-Saudi bilateral trade ($12.9 billion in 2024) potentially subject to political conditions
- Saudi influence over global petroleum markets affecting India’s energy security
India’s Ministry of External Affairs spokesman Randhir Jaiswal stated India would “comprehensively study the implications of this development for our national security and regional stability.”
Stimson Center Senior Fellow Asfandyar Mir encapsulates Indian concerns: “Pakistan has secured formal Saudi alliance backing precisely when facing potential Indian military action, significantly complicating future India-Pakistan strategic dynamics and introducing new variables into conflict scenarios.”
Regional Power Balance Analysis
| Regional Actor | Military Strength | Nuclear Status | Strategic Influence | Alliance Positioning |
| Pakistan | 600,000+ active personnel, Advanced missile systems | Nuclear-armed since 1998 (165+ warheads) | South Asia expanding to Middle East | China, Saudi Arabia |
| Saudi Arabia | Advanced military technology, Substantial defense spending | Non-nuclear (NPT signatory) | Gulf leadership, Islamic world influence | Pakistan, traditional U.S. ties |
| Israel | Technologically advanced military, Regional dominance | Undeclared nuclear program | Middle East strategic control | United States, Abraham Accords partners |
| Iran | Large conventional forces, Regional proxy networks | Nuclear program (weapons capability disputed) | Middle East influence operations | Russia, China partnerships |
| India | 1.4 million personnel, Growing defense capabilities | Nuclear-armed since 1974 (170+ warheads) | South Asian dominance, Indo-Pacific role | United States, Quad partnerships |
Historical Foundation: Decades of Military Cooperation
The current agreement builds upon nearly six decades of sustained military cooperation and strategic partnership development.
Historical Evolution Timeline
| Period | Key Milestone | Strategic Development | Long-term Impact |
| 1967-1980 | Military training program initiation | Pakistan begins systematic Saudi personnel training | Foundation for deep military relationship |
| 1981-1990 | Formal defense cooperation framework | Institutional military cooperation establishment | Permanent Pakistani advisory presence |
| 1991-2001 | Gulf War collaboration and expansion | Enhanced cooperation during regional crisis | Demonstrated alliance operational value |
| 2002-2014 | Post-9/11 security partnership | Intelligence sharing and counter-terrorism coordination | Operational cooperation against common threats |
| 2015 | Yemen intervention parliamentary decision | Pakistan maintains strategic autonomy within alliance | Precedent for independent decision-making |
| 2025 | Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement | Formal mutual defense treaty with binding obligations | Legal framework for comprehensive cooperation |
Military Training Legacy: Pakistan has trained over 8,000-10,000 Saudi military personnel across all service branches since 1967, with current deployment maintaining 1,500-2,000 Pakistani military advisors in Saudi Arabia.
Dr. Mohammed Al-Qubaiban (Saudi Military Affairs Expert) characterizes the relationship: “Saudi Arabia possesses advanced technology and conventional capabilities, while Pakistan represents a nuclear-armed state with demonstrated military expertise. This agreement signals Saudi Arabia’s strategic autonomy in selecting security partnerships based on national interests.”
U.S. Strategic Position: Influence Decline and Policy Implications
Washington’s absence of official response to this historic agreement reveals the extent of American influence erosion in traditional spheres of strategic interest.
American Strategic Credibility Assessment
Traditional U.S. responses to major Gulf security developments included immediate State Department assessments, National Security Council analysis, and Pentagon strategic evaluations. The complete silence regarding this agreement indicates:
- Substantially reduced capacity to influence Gulf security decision-making
- Recognition that criticism might accelerate allied diversification efforts
- Internal policy divisions regarding appropriate response strategies
- Acknowledgment that traditional alliance structures face fundamental challenges
Independent Security Analyst Sahar Khan identifies the credibility deficit: “Pakistan maintains significant credibility challenges in Washington, exacerbated by Biden administration sanctions imposed seven times on Pakistani entities over ballistic missile development. This agreement will not improve that relationship.”
Gulf Diversification from U.S. Dependence
The agreement represents broader Gulf strategic recalculation:
Traditional Security Model:
- Exclusive reliance on U.S. military presence and security guarantees
- Bilateral arrangements providing bases and energy access in exchange for protection
- Limited indigenous defense capabilities and regional coordination
Emerging Diversified Framework:
- Multiple security partnerships with regional powers
- Indigenous defense capability development and regional integration
- Reduced dependence on Western weapons systems with operational restrictions
Expert Analysis: International Perspectives
Leading international experts have provided comprehensive analysis of this strategic development:
U.S. Strategic and Security Analysts
Asfandyar Mir, Senior Fellow, Stimson Center (Washington, D.C.): “Pakistan previously maintained mutual defense treaties with the United States during the Cold War, but they dissolved by the 1970s. Despite extensive defense cooperation with China, Pakistan lacks formal mutual defense agreements, making this Saudi arrangement historically significant and representing a watershed moment for both nations.”
Edmund Fitton-Brown, Senior Fellow, Foundation for Defense of Democracies: “While Saudi-Pakistani relations have long been close, mutual support has faced limitations. This mutual defense pact will likely remain primarily symbolic, with main applications in non-belligerent areas such as training programs and defense procurement rather than active military operations.”
Middle Eastern Military and Security Experts
Dr. Hesham al-Ghannam, Director General, Security Research Center: “This defense agreement fundamentally reshapes the Middle Eastern deterrence equation, altering regional security calculations and establishing new patterns of strategic cooperation that extend beyond traditional alliance structures.”
Pakistani Strategic Defense Experts
Maleeha Lodhi, Former Pakistani Ambassador to the United States: “Pakistan has evolved from regional South Asian power to security provider for broader Middle Eastern stability, representing a fundamental transformation in strategic orientation and international security responsibilities.”
Defense Analyst Sohail Muhammad Ali: “This represents the most significant defense agreement in Pakistan’s history, reflecting international recognition of Pakistan’s defense capabilities and strategic value as a security partner for major regional powers.”
International Academic Perspectives
Muhammad Faisal, South Asia Security Researcher, University of Technology Sydney: “These regional developments have exacerbated Gulf states’ security concerns while undermining confidence in the U.S. security umbrella. Regional countries such as Pakistan, Turkey, and Egypt are emerging as natural security partners for Gulf states seeking alternatives to traditional arrangements.”
Future Strategic Implications and Regional Consequences
The Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement extends far beyond bilateral cooperation, signaling fundamental Middle Eastern and South Asian security architecture restructuring.
Regional Security Architecture Evolution
Immediate Operational Changes:
- Expanded Pakistani military presence in Saudi Arabia from current 2,000 to potentially 5,000+ personnel
- Enhanced joint military exercises incorporating advanced warfare scenarios
- Integrated intelligence operations centers for real-time threat assessment
- Coordinated defense industrial development and technology transfer programs
Economic Integration Acceleration:
- Pakistani defense industry potential for significant Saudi investment and orders
- Saudi financing of Pakistani missile and drone development programs
- Restructured energy agreements linking defense cooperation with economic benefits
- Joint manufacturing ventures in both countries for defense equipment production
Template for Regional Partnership Expansion
This agreement may serve as a model for similar arrangements:
- Pakistan potentially developing comparable agreements with UAE and Qatar
- Turkey and Egypt pursuing formalized Gulf partnerships
- Iran accelerating alliance-building with Russia and China as counterbalance
- India seeking enhanced partnerships to counter Pakistan-Saudi cooperation
Implications for Religious Tourism and Bilateral Relations
The enhanced strategic partnership carries significant implications for Pakistani pilgrims and bilateral religious cooperation.
Hajj and Umrah Enhancement Framework
The strengthened defense alliance will likely improve religious tourism arrangements:
Security Improvements:
- Enhanced protection for Pakistani pilgrims during religious seasons
- Coordinated security planning for large-scale religious gatherings
- Joint counter-terrorism efforts targeting threats to holy sites
Administrative Benefits:
- Streamlined visa processing for Pakistani religious travelers
- Improved coordination for managing 180,000+ annual Pakistani Hajj pilgrims
- Enhanced services at airports and religious sites for Pakistani visitors
Diplomatic Integration:
- Religious cooperation as diplomatic tool for broader strategic objectives
- Islamic banking and finance expansion beyond current $2.3 billion bilateral trade
- Coordination through Organization of Islamic Cooperation for regional influence
Strategic Assessment: Reshaping Global Security Architecture
The Pakistan-Saudi Arabia Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement represents more than regional realignment—it signals fundamental transformation in global security structures and alliance systems.
Global Strategic Implications
For the United States:
- Clear challenge to American Middle Eastern dominance and influence
- Demonstration of alliance limitations when partners seek security alternatives
- Potential acceleration of reduced U.S. military presence in Gulf region
For China and Russia:
- Validation of South-South cooperation approaches independent of Western frameworks
- Enhanced opportunities for defense technology transfer and military equipment sales
- Demonstration of multipolar alliance structure viability
For Regional Stability:
- New deterrence calculations incorporating Pakistan-Saudi cooperation
- Potential for increased regional arms competition and alliance-building
- Fundamental shift from unipolar to multipolar Middle Eastern security arrangements
Long-term Strategic Projections
By 2030, this agreement may catalyze:
- Substantial reduction in U.S. military deployment across Gulf region
- Multiple regional security arrangements operating independently of Western mediation
- Nuclear deterrence frameworks incorporating regional alliance structures
- Global energy and trade patterns adapting to new strategic partnership realities
This Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement marks a definitive moment in contemporary international relations, establishing precedent for regional power cooperation independent of traditional Western alliance structures and signaling the emergence of a multipolar global security architecture that will define international relations for the coming decade.
The agreement’s ultimate impact will depend on how effectively both nations manage their expanded strategic commitments while navigating complex regional relationships and global power dynamics. Success could establish a new model for international cooperation, while failure might contribute to increased regional instability and great power competition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the defense agreement involve nuclear weapons sharing between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia?
The agreement establishes extended deterrence mechanisms rather than physical weapons transfer. The Pakistani Defense Minister’s confirmation that nuclear capabilities will be “absolutely available” creates strategic uncertainty for potential adversaries regarding Pakistani nuclear response to Saudi threats. This arrangement parallels Cold War U.S.-European extended deterrence, operating through alliance credibility and strategic ambiguity rather than actual weapons deployment or sharing arrangements.
What specific factors led to Saudi Arabia formalizing this strategic alliance at this time?
Israel’s September 9, 2025 attack on Qatar fundamentally undermined Gulf state confidence in U.S. security guarantees, occurring despite substantial American military presence at Al Udeid Air Base. This demonstrated traditional security arrangement limitations, compelling Saudi Arabia to pursue alternative partnerships with regional powers capable of providing credible defense commitments independent of Western political constraints and institutional frameworks.
How does this agreement impact existing Pakistan-India strategic dynamics and regional stability?
The agreement significantly destabilizes South Asian strategic equilibrium by providing Pakistan formal Saudi backing immediately following their May 2025 four-day military confrontation. Indian strategic planners must now incorporate Saudi financial resources, diplomatic influence, and potential military support into Pakistan conflict scenarios, fundamentally altering regional balance of power calculations and crisis escalation management procedures.
Is this the first comprehensive defense cooperation arrangement between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia?
Pakistan and Saudi Arabia have maintained military cooperation since 1967, with Pakistani forces training over 8,000 Saudi personnel across multiple decades. However, this constitutes their first formal mutual defense treaty establishing binding legal obligations for mutual protection during conflicts, representing substantial escalation from previous training, advisory, and informal cooperation to comprehensive collective defense commitments.
What implications does this agreement hold for traditional U.S. security arrangements in the Middle East?
The agreement signals substantial decline in U.S. regional influence, demonstrated by Washington’s complete policy silence regarding this historic development. Regional powers are developing independent strategic partnerships without seeking American approval or consultation, potentially precipitating reduced U.S. military presence and diminished American control over Middle Eastern security architecture as multipolar arrangements replace traditional unipolar alliance structures.